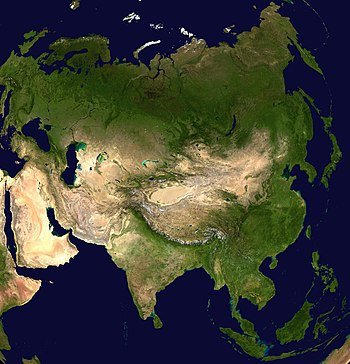
Geography of Asia, Asia is the largest of the world’s continents. It can be divided into five major physical regions: mountain systems; plateaus; plains, steppes, and deserts; freshwater environments; and saltwater environments.
Physical Geography of Asia
- Asia is the largest continent on Earth, making up the eastern portion of the Eurasian supercontinent. It can be divided into five major physical regions: mountain systems, plateaus, plains, steppes, deserts, freshwater environments, and saltwater environments.
- The continent is bordered by the Arctic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans, and its western border is defined by the Ural Mountains, the Caucasus Mountains, and the Caspian and Black Seas.
- Asia is also the world’s most populous continent, home to roughly 60% of the total population.
- It is geographically diverse, with the highest and lowest points on Earth, the longest coastline of any continent, and a wide range of climatic extremes and vegetation.
- The continent is divided into various sub-regions, including Western Asia, Central Asia, Southern Asia, Eastern Asia, Southeastern Asia, and Northern Asia.
- Oceans (Pacific, Indian, and Arctic) surround Asia on three sides.
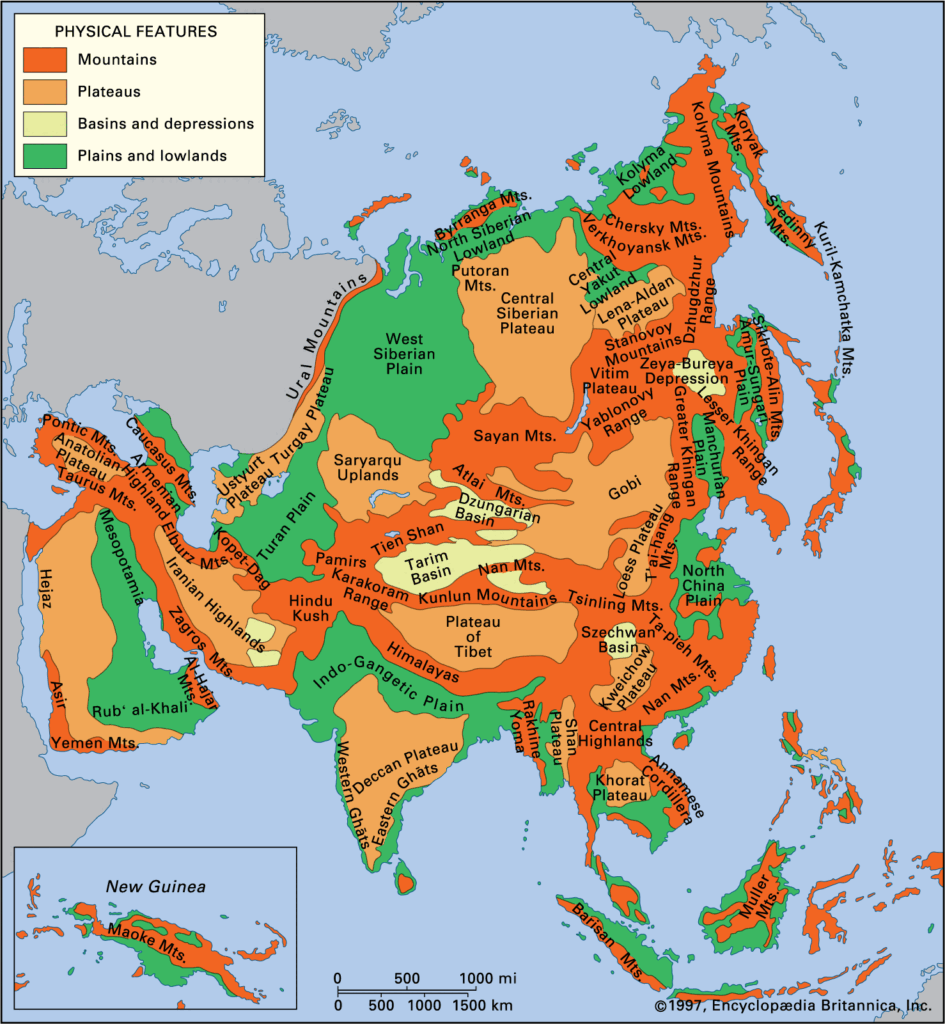
What are the major mountain systems in Asia?
The major mountain systems in Asia include:
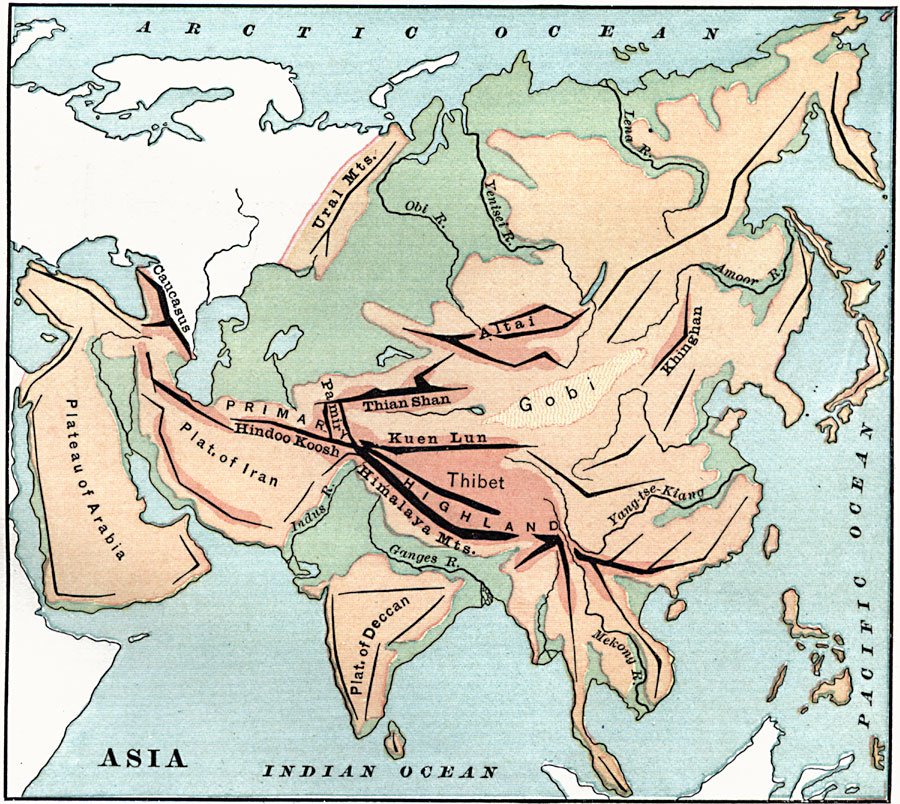
- The Himalayas are home to the world’s highest peak, Mount Everest, and span five countries: India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, and Pakistan.
- The Karakoram Range: is located in Pakistan, India, China, and Afghanistan
- The Hindu Kush is primarily located in Afghanistan, with many peaks above 7,000 meters.
- The Ural Mountains form a natural border between Asia and Europe.
- The Altai Mountains: Spanning Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan.
- The Pamir Mountains are known as the “Roof of the World” and are primarily located in Tajikistan.
- The Kunlun Mountains are one of the longest mountain chains in Asia, extending more than 3,000 kilometers.
- The Tian Shan is a central Asian range home to some of the world’s highest peaks.
These mountain ranges are not only important parts of Asia’s geographic landscape but also of its cultural diversity and essential resources.
major plateaus in Asia?
Some of the major plateaus in Asia include:
- Tibetan Plateau: It is the highest plateau in Asia, with an average elevation of more than 4,500 meters. The plateau is surrounded by imposing mountain ranges.
- Mongolian Plateau: Covering an area of more than 3,200,000 square kilometers, it is divided between China, Mongolia, and Russia. The terrain gradually decreases from west to east, and there are many rivers and lakes on the plateau.
- Iranian Plateau: This plateau covers more than 3.6 million square kilometers, encompassing most of Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. It is not uniformly flat, containing some high mountains and low river basins. The highest mountain peak is Damavand, at 5,610 meters.
- Deccan Plateau: Located in India, it makes up most of the southern part of the country. The plateau’s average elevation is about 600 meters and is bordered by three mountain ranges: the Satpura Range in the north, and the Eastern and Western Ghats on either side.
These plateaus are significant geographical features, offering distinctive sceneries and climatic conditions due to their wide variation in size and geographic features.
Major plains in Asia
Some of the major plains in Asia include:
- Indo-Gangetic Plain: One of the most extensive and fertile plains in the world, covering parts of Pakistan, India, Nepal, and Bangladesh.
- North China Plain: A large plain in eastern China, where the Yellow River and its tributaries flow.
- West Siberian Plain: Considered one of the world’s largest areas of continuous flatland, it is located in central Russia and contains some of the world’s largest swamps and flood plains.
- Central Asia: Dominated by a steppe landscape, it is a large area of flat, unforested grassland.
These plains are significant for agriculture, human settlement, and the overall geographic diversity of the continent.

Pingback: contribution of Immanuel Kant in geography - Geography Study
Pingback: climate of Asia - Geography Study
Pingback: 10 Highest Mountains In The United States - Geography Study
Pingback: Oceanic density and salinity - Geography Study